Test Prep courses
Intensive preparation for the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) actually changes the microscopic structure of the brain, physically bolstering the connections between areas of the brain important for reasoning, according to neuroscientists at the University of California, Berkeley.
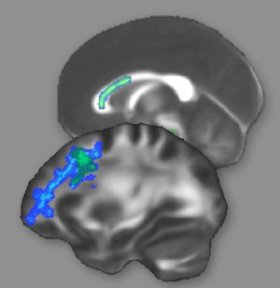
The results suggest that training people in reasoning skills – the main focus of LSAT prep courses – can reinforce the brain’s circuits involved in thinking and reasoning and could even up people’s IQ scores.
“The fact that performance on the LSAT can be improved with practice is not new. People know that they can do better on the LSAT, which is why preparation courses exist, ” said Allyson Mackey, a graduate student in UC Berkeley’s Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute who led the study. “What we were interested in is whether and how the brain changes as a result of LSAT preparation, which we think is, fundamentally, reasoning training. We wanted to show that the ability to reason is malleable in adults.”
The new study shows that reasoning training does alter brain connections, which is good news for the test prep industry, but also for people who have poor reasoning skills and would like to improve them. The findings are reported today (Wednesday, Aug. 22) in the open access journal .
“A lot of people still believe that you are either smart or you are not, and sure, you can practice for a test, but you are not fundamentally changing your brain, ” said senior author Silvia Bunge, associate professor in the UC Berkeley Department of Psychology and the Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute. “Our research provides a more positive message. How you perform on one of these tests is not necessarily predictive of your future success, it merely reflects your prior history of cognitive engagement, and potentially how prepared you are at this time to enter a graduate program or a law school, as opposed to how prepared you could ever be.”
John D. E. Gabrieli, a professor of cognitive neuroscience at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who was not involved in the research, noted that researchers in the past have shown anatomical changes in the brain from simpler tasks, such as juggling or playing a musical instrument, but not for tasks as complex and abstract as thinking or reasoning, which involve many areas of the brain.
“I think this is an exciting discovery, ” he said. “It shows, with rigorous analysis, that brain pathways important for thinking and reasoning remain plastic in adulthood, and that intensive, real-life educational experience that trains reasoning also alters the brain pathways that support reasoning ability.”
You might also like